The HLA-C Gene
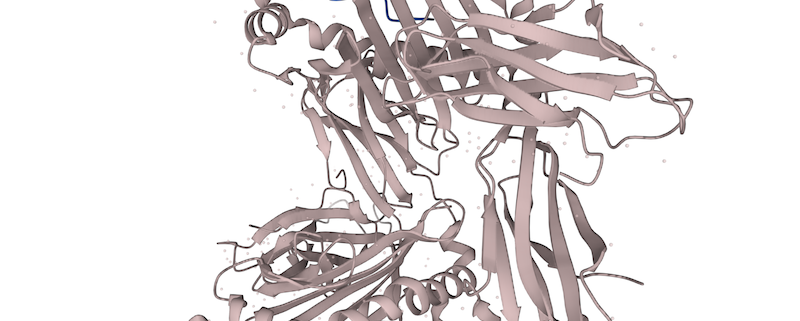
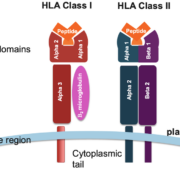
The HLA-C gene is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene located on human chromosome 6. It is a member of the MHC Class I family of genes, which are responsible for the recognition and presentation of antigens to the immune system. The HLA-C gene is composed of two exons, which encode the heavy and light chain of the HLA-C protein. The heavy chain is composed of three domains, while the light chain is composed of one domain. The HLA-C gene is involved in the immune response to foreign antigens, and it is responsible for the recognition and presentation of peptides to T-cells.
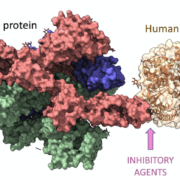
The HLA-C gene encodes the HLA-C protein, which is a cell surface protein that is involved in the recognition of foreign antigens. The HLA-C protein binds to peptides in the endoplasmic reticulum and presents them to T-cells. This is important for the recognition of foreign antigens, as well as for the development of tolerance to self-antigens. The HLA-C protein is also involved in the regulation of natural killer cell activity.
The HLA-C gene is highly polymorphic, meaning that there are many different alleles. This polymorphism is important for the recognition of foreign antigens, as it increases the chances of the host identifying the antigen. The HLA-C genes are also important for the development of autoimmune diseases, as certain HLA-C alleles are associated with increased risk of developing certain autoimmune diseases.
The HLA-C gene has also been implicated in a variety of diseases, such as type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Certain HLA-C alleles have been associated with increased risk of developing these diseases. In addition, the HLA-C gene has been linked to various infectious diseases, including HIV, hepatitis B, and tuberculosis.
Overall, the HLA-C gene is an important gene involved in the recognition and presentation of foreign antigens to the immune system. It is also associated with a variety of diseases, including autoimmune diseases and infectious diseases. The HLA-C gene is highly polymorphic, which increases the chances of the host identifying the antigen. This polymorphism is important for the development of tolerance to self-antigens, as well as for the recognition of foreign antigens.


 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!