HLA Susceptibility in SARS-CoV-2
Nguyen et al. recently published a paper “Human leukocyte antigen susceptibili8ty map for SARS-CoV-2” in the Journal of Virology. Using in-silico methods, they assessed the binding affinities of MHC Class I alleles (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C) with all known SARS-CoV-2 8-12mer peptides from the full SARS-CoV-2 proteome. Presumably, the binding affinities of MHC Class I molecules to SARS-CoV-2 peptides are correlated with COVID-19 immunity and with the severity of the disease.
Methods
The researchers obtained the SARS-CoV-2 proteome from the NCBI RefSeq database under accession number NC_045512.2. They k-merized the full proteome into a set of 8-12mer peptides. Then they predicted the binding affinity of the SARS-CoV-2 peptide set to MHC Class I molecules with netMHCpan . The peptide-Class I binding affinities were differentiated into tight binding peptides (<50 nM) and loosely binding peptides (>= 50 nM – <500 nM).
Results
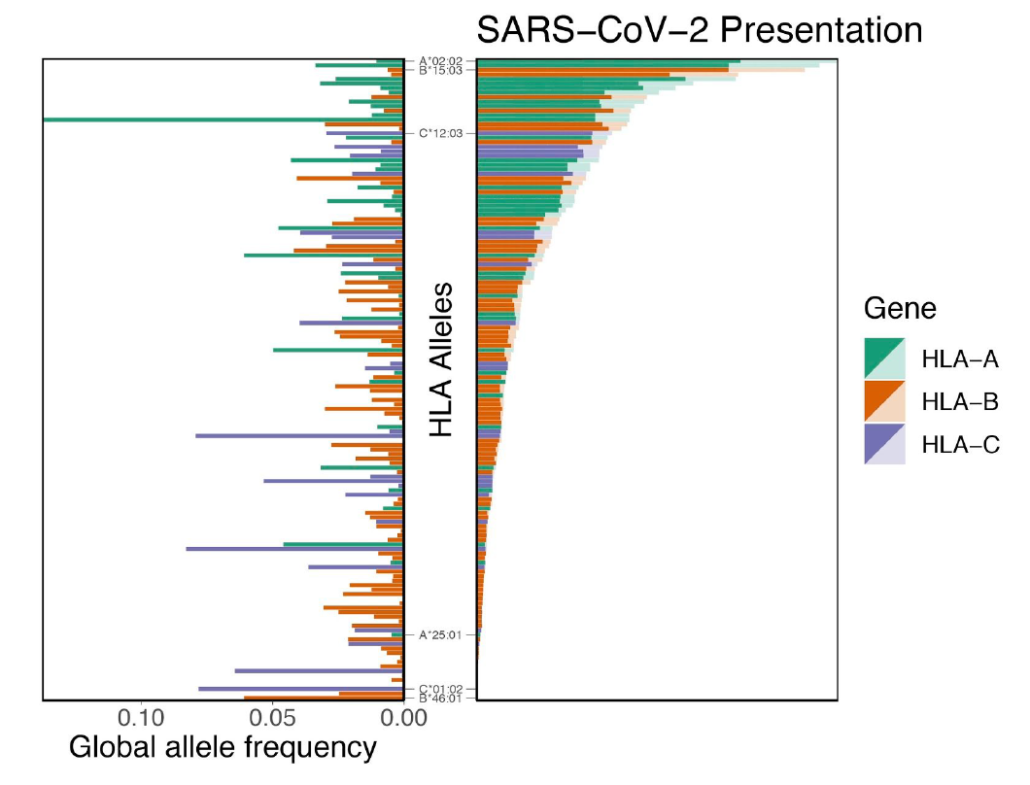
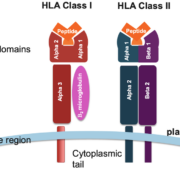
Fig. 1 SARS-CoV-2 Presentation
The right-side panel in Fig. 1 shows the number of SARS-CoV-2 peptides that bind to each HLA allele. The 8-12mer peptides were obtained from the full SARS-CoV-2 proteome. There are 145 HLA alleles in the list. The alleles are arranged in descending order by the number of bound peptides. Alleles with the greatest number of bound peptides are shown at the top, and alleles with the least number of bound peptides are shown at the bottom. Class I alleles are color-coded as HLA-A (green), HLA-B (orange) and HLA-C (purple). Dark and light shading indicate tightly bound (<50 nM) and loosely bound (>= 50 nM and <= 500 nM) peptides.
Based on the predicted binding affinities of SARS-CoV-2 peptides with MHC Class I alleles, the authors suggest that three alleles may be associated with increased disease severity, namely,
- HLA-A*25:01
- HLA-B*46:01
- HLA-C*01:02
and three alleles may be associated with decreased disease severity
- HLA-A*02:02
- HLA-B*15:03
- HLA-C*12:03
Also, HLA-A*02:02 shows the greatest number of predicted bound peptides from the SARS-CoV-2 proteome. And HLA-B*46:01 shows the least number of predicted bound peptides from the SARS-CoV-2 proteome.
The authors acknowledge that there are limitations to their findings. The study is entirely theoretical in nature and did not include real clinical data to validate their results. The study design is dependent on algorithmic limitations of the MHC binding prediction servers, and they did not include genotypic heterogeneity in their analyses.
Nevertheless, this paper highlights several MHC Class I alleles that could be used in clinical studies to identify patients who may be at higher risk, or lower risk, for COVID-19. If these alleles are subjected to experimental validation and shown to be correlated with disease severity, then they may be used to identify high-risk and low-risk patients. In The Sequencing Center we have clients who are performing these types of experimental projects with Next Generation Sequencing methods.


 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!