Unraveling the Complexities of HLA Mutations and Its Implications in Disease Susceptibility
As research into human leukocyte antigens (HLAs), hugely important molecular markers of the immune response, continues to grow, it consistently unveils a multifaceted array of genetic expressions that contribute to disease susceptibility. HLAs, crucial components of the immune system, characterize an individual’s specific immune response to pathogens and foreign substances. The identification of HLA mutations and their correlation with the onset of various diseases has paved the way for a deeper understanding of disease susceptibility.
The complex architecture of the HLA system, with its excessive polymorphisms, poses significant challenges to disease association studies. However, recent advancements in sequencing technology and statistical methods have facilitated more direct and comprehensive evaluations of the HLA-disease associations. A major breakthrough was the discovery of rs9271366, an HLA-DP variant, which identifies individuals with a high predisposition towards chronic hepatitis B.
Chronic Hepatitis B and HLA-DP
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) remains a significant global health concern, predominantly due to the ability of the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) to persistently infect the liver cells and establish chronicity. It is estimated that over 240 million people worldwide are chronically infected with HBV, with over 780,000 succumbing to HBV-induced liver diseases every year.
However, not everyone exposed to the virus will end up with CHB. This variation in susceptibility led scientists to consider host genetic factors, particularly the HLA system, as contributing elements. The landmark finding that associated the HLA-DP polymorphism rs9271366 with increased susceptibility to CHB offered an essential clue to understanding why some individuals are prone to chronic disease while others aren’t. The presence of rs9271366 might affect the functional properties of antigen presentation, hence influencing the immune response to HBV invasion and predisposing individuals to chronic infection.
Furthering the Understanding
Advanced technological and algorithmic systems have unlocked the potential to better understand the implications of this HLA variant. They allow for the prediction of peptide binding affinities across a large spectrum of HLA alleles, and likewise provide a comprehensive picture of the extent HLA-DP mutation influences the immune response. While these developments warrant apprehension about the risks associated with HLA mutations, they equally bring optimism, as a thorough comprehension of these genetic elements could open the doors to personalized medicine.
Implications for the Future
Understanding the role of HLA mutations in disease susceptibility could significantly impact the field of personalized medicine, allowing for targeted prevention strategies. For individuals carrying such genetic variants, enhanced surveillance or early intervention could potentially reduce their chances of developing diseases. For diseases with high morbidity and mortality like CHB, understanding the HLA-DP mutation can inform the development of more effective vaccines and therapeutic strategies. Additionally, this knowledge could significantly improve our understanding of disease progression and response to treatment.
Wrapping Up
Unraveling the intricate relationship between HLA mutations and disease susceptibility offers exciting prospects in disease prediction, prevention, and treatment. With technological advancements providing more robust tools for exploration, our understanding and management of these relationships can only continue to grow.

 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center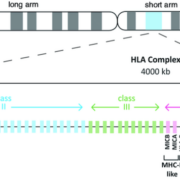

 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!