HLA Typing: Exploring Disease States Associated with Variants of the HLA-B Gene
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) typing is an essential tool in understanding genetic susceptibility to diseases, as it identifies specific alleles associated with various disease states. Among the HLA genes, the HLA-B gene has been extensively studied due to its crucial role in immune response and its link to numerous diseases. This white paper investigates the disease states associated with variants on the HLA-B gene, focusing on the importance of accurate HLA typing for optimal clinical outcomes.
Background on the HLA-B Gene
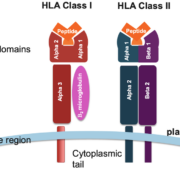
The HLA-B gene, located within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on Chromosome 6, encodes for the HLA-B protein, a critical component of the immune system. This protein presents antigenic peptides to T-cells, initiating an immune response against foreign substances or pathogens. Due to the high polymorphism of the HLA-B gene, it is essential to employ HLA typing techniques to pinpoint specific alleles associated with various disease states.
Role of HLA Typing in Disease Association
HLA typing is a method that identifies specific HLA alleles or groups of alleles to predict the genetic susceptibility of an individual to certain diseases. As the HLA-B gene plays a pivotal role in immune response, accurate HLA typing is crucial in determining disease risk, optimizing treatment strategies, and improving clinical outcomes for various conditions.
HLA-B Gene Variants and Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by the body’s immune system attacking its tissues. Several studies have demonstrated that certain HLA-B gene variants, such as HLA-B*27, are strongly associated with an increased risk for autoimmune diseases like ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, and anterior uveitis. Therefore, HLA typing can be useful in early diagnosis and management of these conditions.
HLA-B Gene Variants and Infectious Diseases
HLA-B gene variants also influence susceptibility to infectious diseases, as these alleles can determine the effectiveness of an individual’s immune response to pathogens. For example, HLA-B57 and HLA-B27 are associated with slower disease progression in HIV-infected individuals, while HLA-B*35 is linked to rapid progression. HLA typing can, thus, provide valuable insights into the prognosis and potential treatment strategies for such infectious diseases.
HLA-B Gene Variants and Transplantation
HLA typing plays a vital role in transplantation medicine, as the compatibility between donor and recipient HLA alleles can significantly impact transplant success. Identifying specific HLA-B gene variants can help reduce the risk of graft rejection and improve transplant outcomes, especially in cases of hematopoietic stem cell and solid organ transplantation.
HLA-B Gene Variants and Drug Hypersensitivity
HLA-B gene variants are also implicated in drug hypersensitivity reactions. For instance, HLA-B57:01 is associated with abacavir hypersensitivity syndrome, while HLA-B15:02 and HLA-B*58:01 are linked to carbamazepine and allopurinol-induced severe cutaneous adverse reactions, respectively. HLA typing can guide clinicians in prescribing appropriate medications and avoiding adverse drug reactions in susceptible patients.
HLA Typing Techniques
Various HLA typing techniques are available, such as serological typing, sequence-specific oligonucleotide probing, sequence-specific priming, and next-generation sequencing. Each method has its advantages and limitations, but the choice of technique depends on the clinical context, the required resolution, and the available resources.
Challenges in HLA Typing
Despite its clinical utility, HLA typing faces several challenges, including the high degree of polymorphism, the presence of rare or novel alleles, and the difficulty in distinguishing between closely related alleles. Additionally, factors such as cost, technical expertise, and turnaround time can impact the accessibility and implementation of HLA typing in routine clinical practice. Continued advancements in genotyping technologies and bioinformatics tools are essential to overcoming these obstacles and enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of HLA typing.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the association between HLA-B gene variants and various disease states highlights the importance of HLA typing in personalized medicine. By identifying specific HLA alleles, healthcare providers can better predict disease susceptibility, tailor treatment strategies, and improve patient outcomes. Continued research and advancements in HLA typing techniques will pave the way for a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between the HLA-B gene and human health, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare systems worldwide.



 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!