Harnessing Long-Read Sequencing in HLA Typing
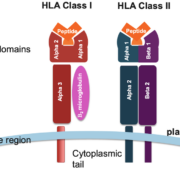
The Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) system holds a significant role in the world of genomics, driving research in areas as diverse as organ transplantation, disease association studies, and immune response. HLA Typing, a method used to identify specific variations of the HLA gene complex in individuals, has historically posed numerous challenges due to the highly polymorphic and complex nature of these genes. The advent of long-read sequencing technology, however, has initiated a transformative shift, offering unique benefits for HLA Typing and propelling advancements in personalized medicine.
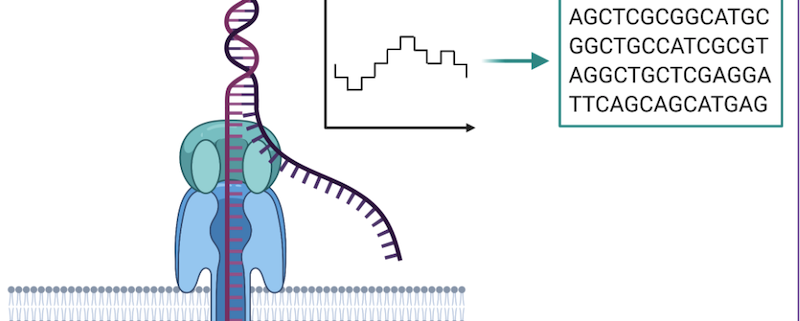
Long-read sequencing, a relatively recent advancement in genomic technology, generates read lengths of tens of thousands of base pairs, compared to the few hundred base pairs of short-read technology. This difference is particularly advantageous for HLA Typing because it facilitates a holistic view of the HLA gene complex. Due to their complexity, HLA genes often harbor multiple polymorphisms within a single gene, making them difficult to accurately sequence with short-read technology. Long-read technology, by contrast, can span these polymorphic regions in a single read, providing a more comprehensive and accurate sequence.
Furthermore, the ability of long-read sequencing to decipher complex genomic regions helps to mitigate the issue of phasing. Phasing, or determining the sequence of alleles on the same chromosome, is crucial in the field of genomics and is particularly important in HLA Typing. With long-read sequencing, researchers can identify and phase multiple alleles simultaneously, improving the accuracy of HLA Typing and reducing the chance of mismatches, which are crucial in applications like organ transplantation.
In addition to accuracy, long-read sequencing technology also enables greater depth in HLA Typing. By generating longer reads, this technology allows for a more comprehensive representation of an individual’s HLA genes, including the characterization of rare and novel HLA alleles. As a result, long-read sequencing not only improves the quality of HLA Typing but also aids in expanding the knowledge of HLA gene diversity, paving the way for more precise disease association studies and improving donor-recipient matching in transplantation medicine.
In summary, the application of long-read sequencing technology in HLA Typing offers significant benefits, enabling a leap forward in genomics and personalized medicine. By providing comprehensive, accurate, phased, and deep insight into the complex HLA gene system, long-read sequencing elevates the quality and scope of HLA Typing. As we continue to unlock the potential of this powerful technology, we are forging a path toward more nuanced understanding and application of the HLA system in disease treatment and prevention, thereby transforming patient outcomes on a global scale.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!