The HLA-DQA1 Gene
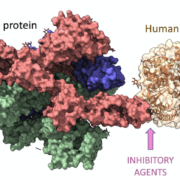
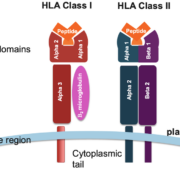
The HLA-DQA1 gene is a member of the HLA gene family, which is located on the short arm of chromosome 6. The gene encodes proteins that are involved in the immune response and are part of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). HLA-DQA1 proteins are primarily expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells. The proteins act as receptors for antigens and help the immune system recognize and respond to foreign substances.
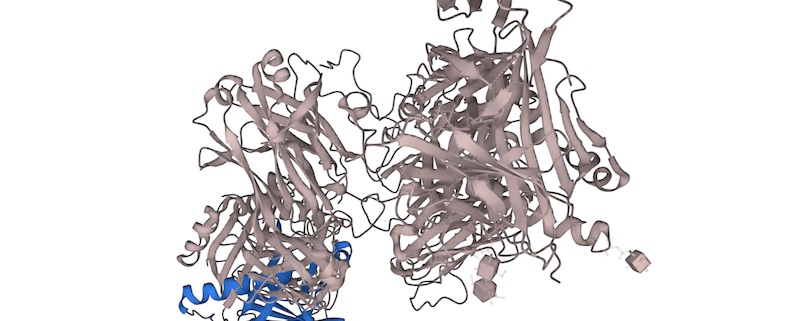
HLA-DQA1 is composed of two exons, which encode the alpha-1 and alpha-2 domains of the protein. The alpha-1 domain is responsible for the recognition of antigenic peptides, while the alpha-2 domain helps to stabilize the peptide-MHC complex. The MHC complex is then presented on the cell surface and recognized by T cells, which can then initiate an immune response.
Variation in the HLA-DQA1 gene is associated with a number of diseases, including type 1 diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, and celiac disease. In type 1 diabetes, variation in the gene is linked to an increased risk of the disease. It is thought that the variation in the gene affects the ability of the immune system to recognize and respond to insulin-producing beta cells, which leads to the destruction of the cells and the development of type 1 diabetes.
HLA-DQA1 is also associated with autoimmune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In SLE, variation in the gene is thought to affect the recognition of self-antigens, which leads to an inappropriate immune response against the body’s own tissues. This can lead to inflammation and tissue damage, which can cause symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes.
HLA-DQA1 is a highly polymorphic gene, which means that there are many different versions of the gene in the population. This variation is important for the immune system, as it allows it to recognize a wide range of antigens. However, the variation can also lead to disease, as discussed above. Thus, it is important to understand the role of HLA-DQA1 in health and disease.


 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!