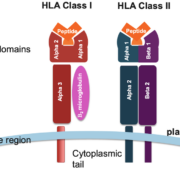
The HLA-DPB1 Gene
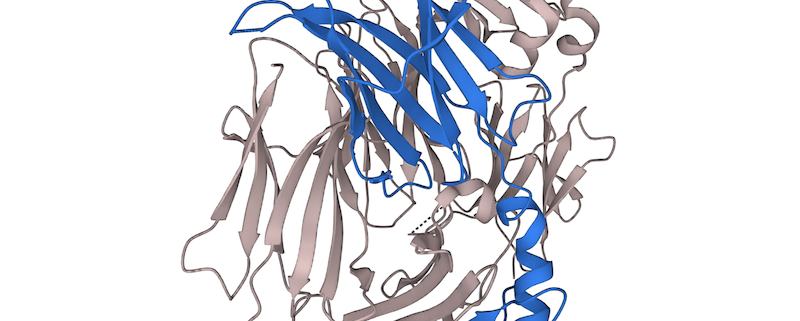
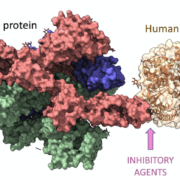
The HLA-DPB1 gene is a gene located on the short arm of the sixth chromosome (6p21.3) and is part of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) major histocompatibility complex (MHC) locus. The HLA-DPB1 gene is important for the immune system as it is involved in the recognition of foreign antigens. Specifically, the HLA-DPB1 gene encodes for the DPB1 molecule, which is a member of the HLA-II family and is involved in the presentation of peptides in the context of the MHC-II antigen-presenting complex. The DPB1 molecule is expressed on the surface of antigen presenting cells and binds to the T cell receptor on T cells, allowing them to recognize foreign antigens.
The HLA-DPB1 gene is highly polymorphic and is associated with many autoimmune and infectious diseases, including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and hepatitis C. In addition, HLA-DPB1 is associated with the susceptibility to a variety of infectious diseases, such as HIV, malaria, and tuberculosis. Because of its polymorphism, the HLA-DPB1 gene is also used for tissue typing and antibody screening for organ transplants.
Several genetic variants of the HLA-DPB1 gene have been identified and are associated with different levels of disease susceptibility. For example, the HLA-DPB1*0401 allele is associated with an increased risk of type 1 diabetes and the HLA-DPB1*0301 allele is associated with a decreased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Additionally, the HLA-DPB1*1402 allele is associated with an increased risk of tuberculosis and the HLA-DPB1*1501 allele is associated with an increased risk of malaria.
The HLA-DPB1 gene has also been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases. For example, the HLA-DPB1*0401 allele has been associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, and the HLA-DPB1*1301 allele has been associated with an increased risk of multiple sclerosis. Additionally, the HLA-DPB1 gene has been associated with the development of certain cancers, such as breast and prostate cancer.
Overall, the HLA-DPB1 gene is an important gene in the immune system and its polymorphism is associated with a variety of diseases and conditions. Its role in the recognition of foreign antigens and its use in tissue typing and antibody screening make it a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.


 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!