What are the Differences Between 2-field and 4-field Reporting for HLA Typing?
As a researcher, you are likely familiar with the importance of HLA typing in various clinical applications, such as transplantation, disease association studies, and pharmacogenomics. Given the critical role that HLA typing plays in these areas, understanding the nuances of reporting methods is vital. In this blog post, we will delve into the differences between 2-field and 4-field reporting for HLA typing, highlighting the implications and benefits of each approach.
A brief overview of HLA typing
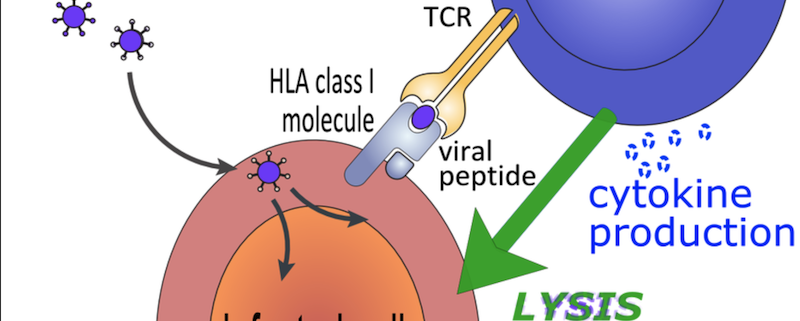
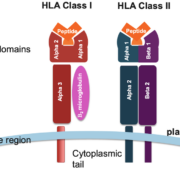
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing refers to the process of identifying the specific alleles present at HLA gene loci, which encode cell surface proteins responsible for immune system regulation. HLA proteins facilitate the recognition and presentation of foreign antigens to immune cells, and consequently, the HLA system is highly polymorphic. Accurate HLA typing is essential for determining compatibility between donors and recipients in organ transplantation and for understanding the genetic basis of various diseases and drug responses.
The importance of allele resolution in HLA typing
The complex nature of the HLA system makes it essential to distinguish between different alleles with high resolution. Allele resolution refers to the level of detail reported in HLA typing results, ranging from low to high resolution. High-resolution typing provides more precise information on the specific alleles present, while low-resolution typing only identifies the broad antigen groups.
2-field reporting for HLA typing
2-field reporting is a high-resolution HLA typing method that identifies alleles based on their protein sequence differences. This reporting format provides information on the first two fields of the allele designation, which represent the allele group (first field) and specific protein sequence (second field). For example, an HLA typing result might be reported as HLA-A*02:01, where ’02’ is the allele group and ’01’ is the specific protein sequence.
The primary advantage of 2-field reporting is its ability to differentiate between alleles that encode distinct protein sequences, which can have significant clinical implications. However, this method does not provide information on nucleotide sequence differences that do not alter the protein sequence.
4-field reporting for HLA typing
4-field reporting is a more comprehensive, high-resolution HLA typing method that identifies alleles based on both protein and nucleotide sequence differences. This reporting format includes the first four fields of the allele designation: the allele group (first field), specific protein sequence (second field), synonymous nucleotide sequence (third field), and non-coding region variations (fourth field).
For example, an HLA typing result might be reported as HLA-A*02:01:01:01. The additional fields provide valuable information on the exact nucleotide sequence of the allele, which can be important for certain applications, such as identifying rare alleles, tracking new mutations, and understanding the genetic basis of disease associations.
Choosing between 2-field and 4-field reporting for HLA typing
The choice between 2-field and 4-field reporting for HLA typing depends on the specific needs of the study or clinical application. In many cases, 2-field reporting may be sufficient for determining donor-recipient compatibility in transplantation or for identifying disease associations. However, 4-field reporting may be more appropriate for certain research applications, particularly those that require detailed information on the nucleotide sequence of HLA alleles.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between 2-field and 4-field reporting for HLA typing is crucial for medical researchers working with this essential aspect of immunogenetics. While both methods provide high-resolution typing, the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of your study or clinical application. As the field of HLA typing continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about advances in typing methods and reporting formats to ensure the most accurate and relevant results for your research.
In summary, 2-field reporting for HLA typing identifies alleles based on protein sequence differences, which is often sufficient for transplantation and disease association studies. On the other hand, 4-field reporting provides additional information on nucleotide sequence differences, including synonymous and non-coding region variations, making it more suitable for certain research applications that require a deeper understanding of HLA allele genetics.


 The Sequencing Center
The Sequencing Center

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!